文章目录
SpringBoot其设计目的是用来简化Spring应用的初始搭建以及开发过程。该框架使用了特定的方式来进行配置,从而使开发人员不再需要定义样板化的配置,提供自动配置的“starter”项目对象模型以简化Maven配置,所谓约定大于配置。
本文重点分析springboot的starter机制,解析它如何把需要的类加载到spring容器中的过程,希望通过一步步分析使大家能够更好的理解其中的原理。
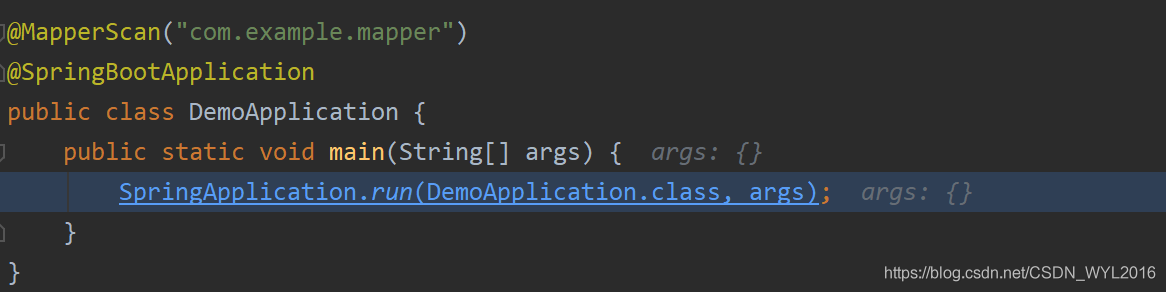
从run方法开始
SpringBoot启动都是通过执行run方法,debug启动从run方法开始看


SpringApplication构造方法
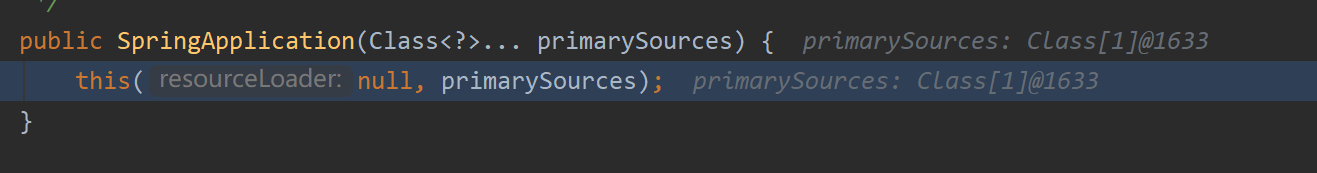
跟了几个方法后,来到SpringApplication的一个构造方法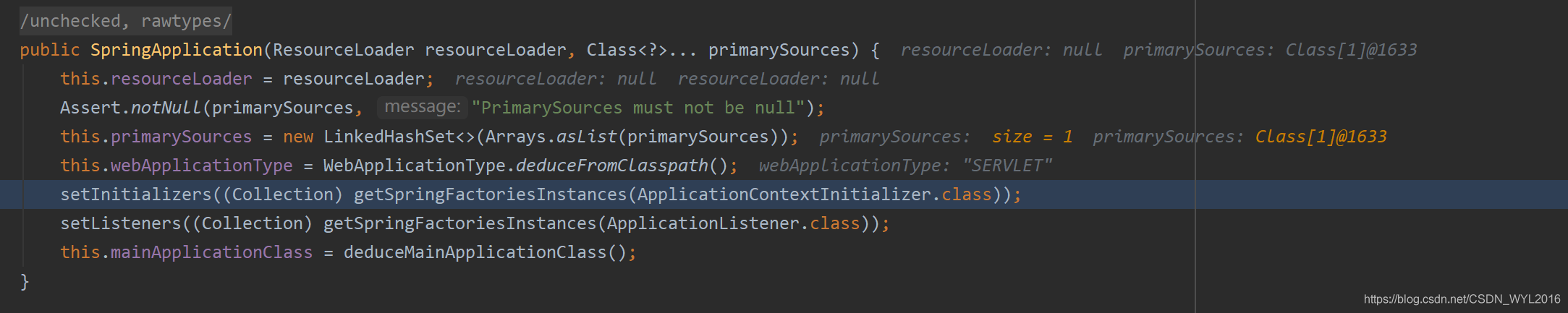
从方法名可以看出,这里要加载对象实例了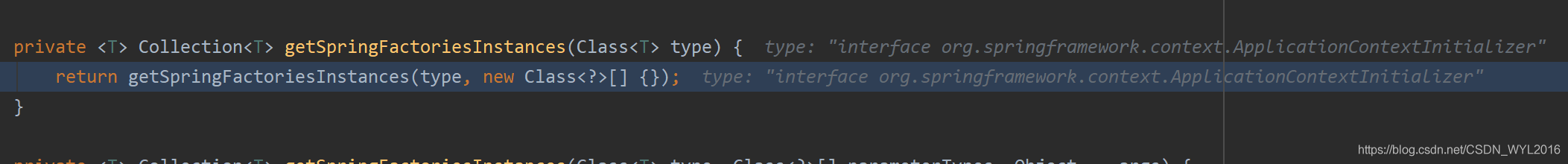
去哪找要加载的对象
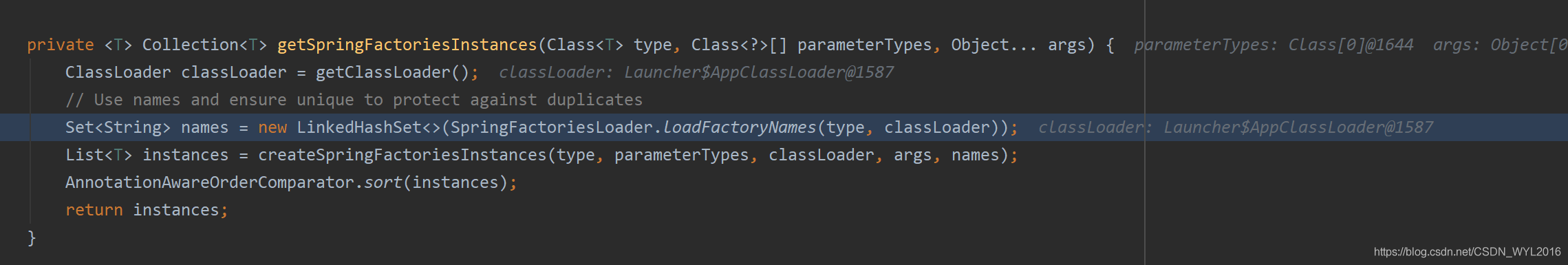

对象在spring.factories文件里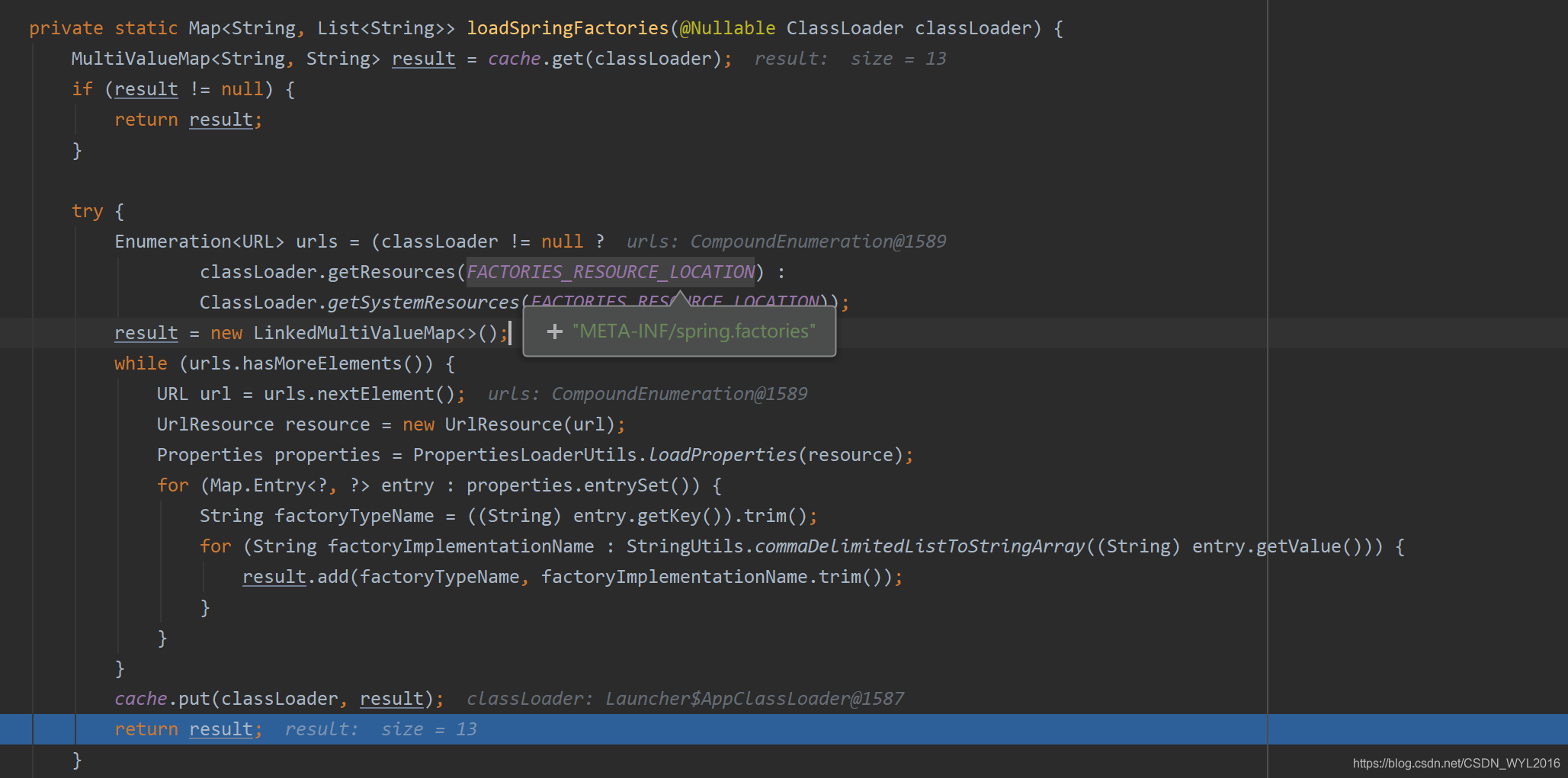
通过SPI机制扫描到META-INF/spring.factories文件中的内容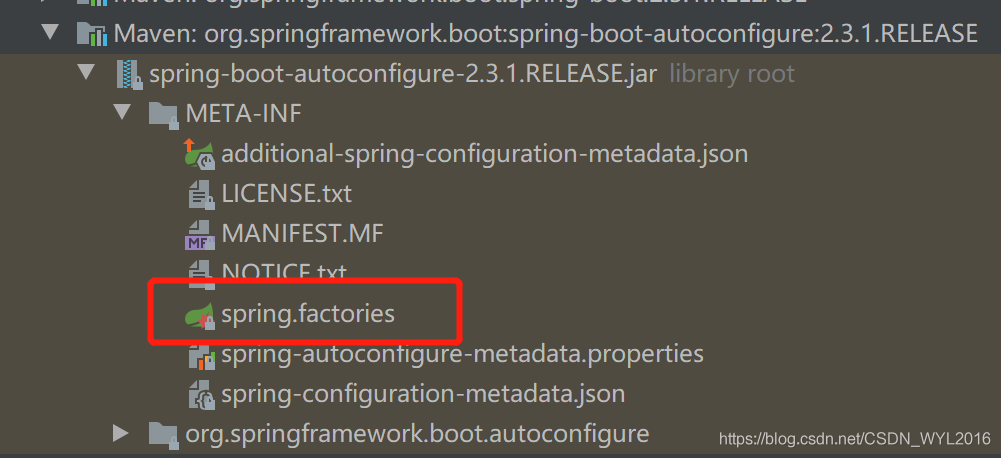
文件中的内容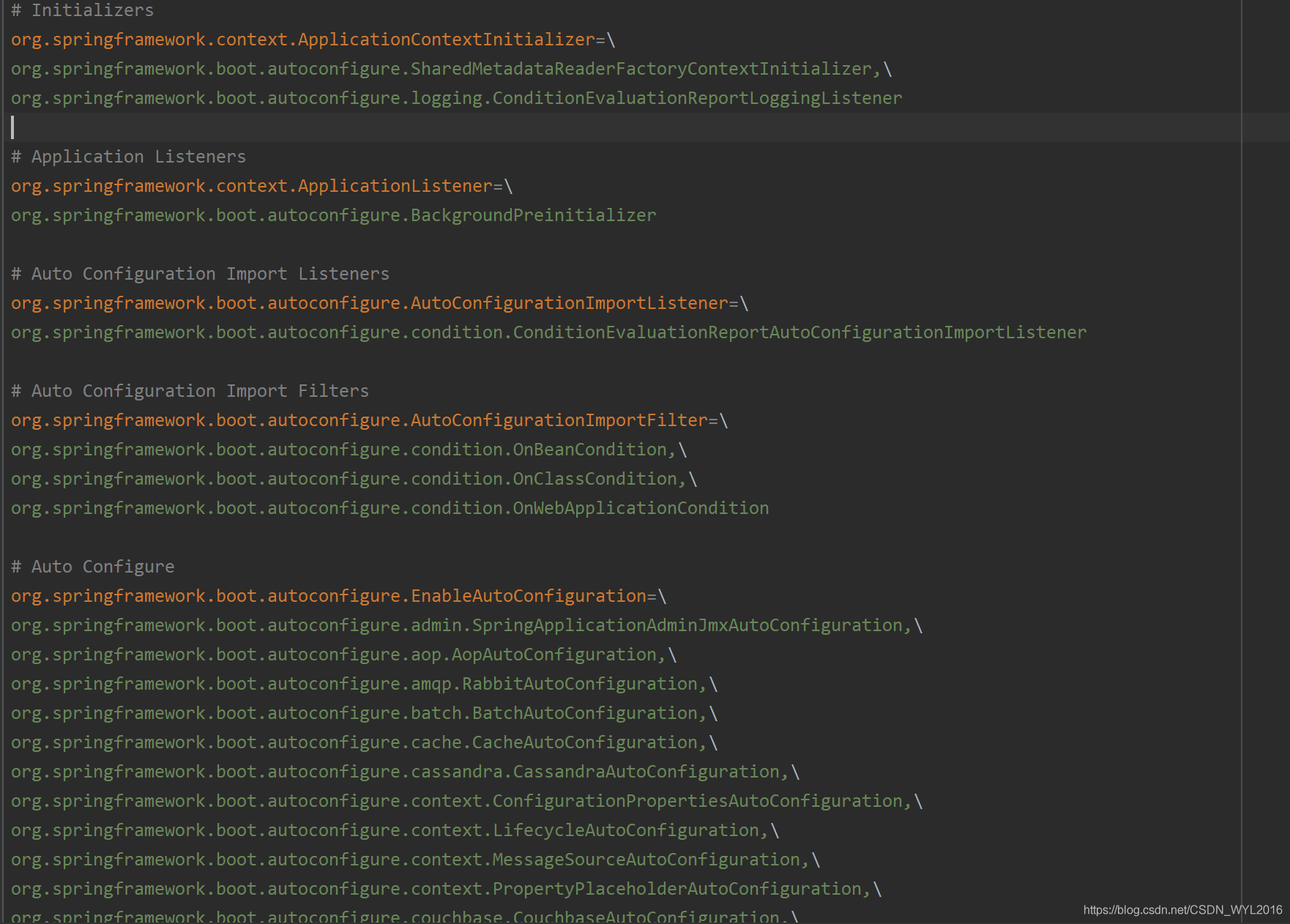
把对象放入Map中
构造方法执行完,META-INF/spring.factories中的类就已经被加载到一个map容器中了。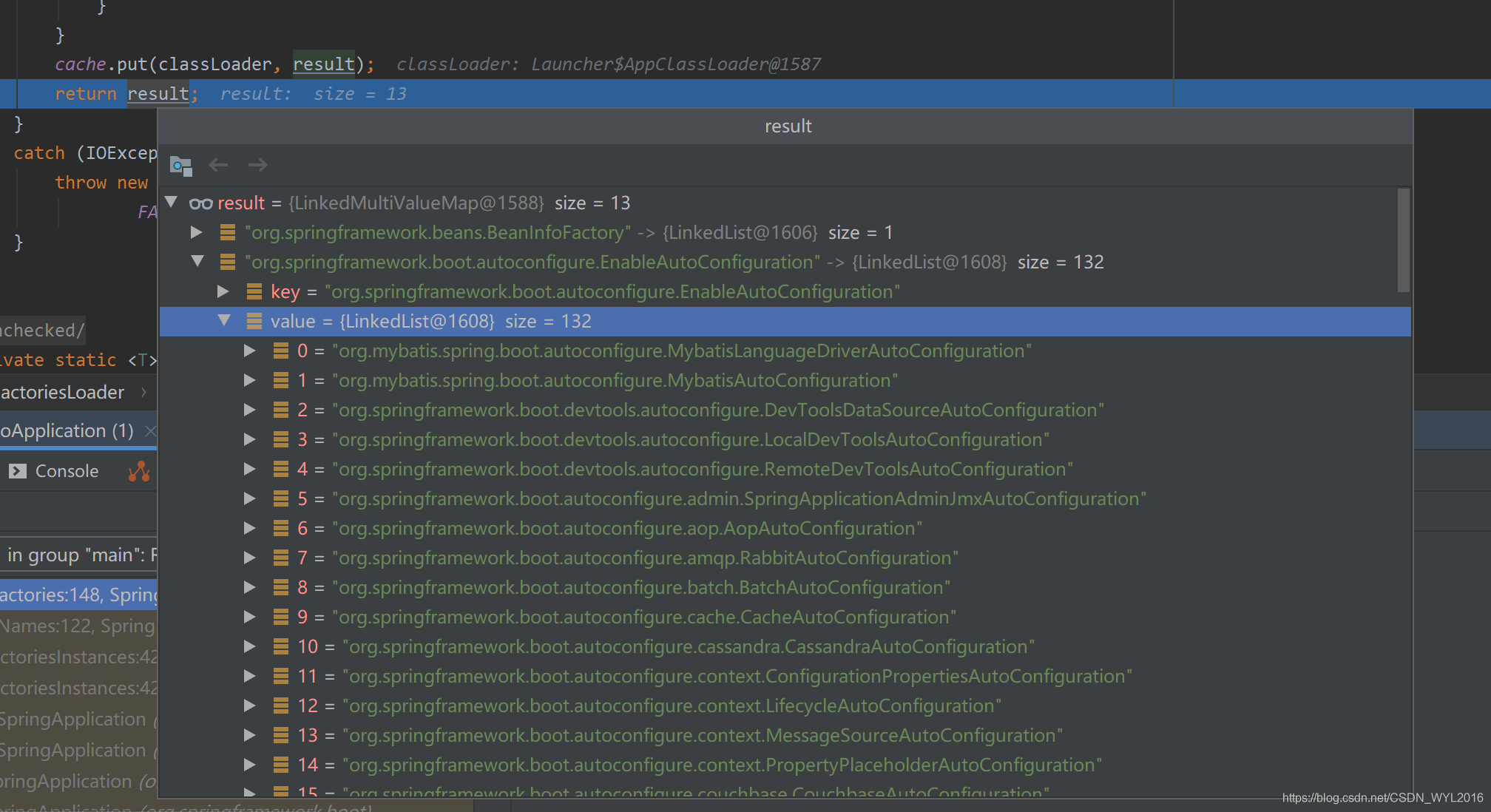
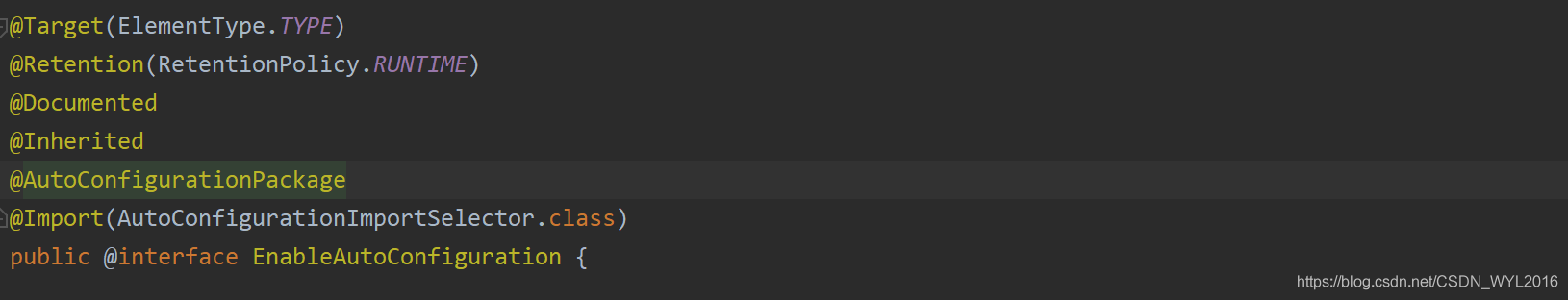
@SpringBootApplication注解的作用
接下来就是@SpringBootApplication注解发挥作用的时候了。
注解点进去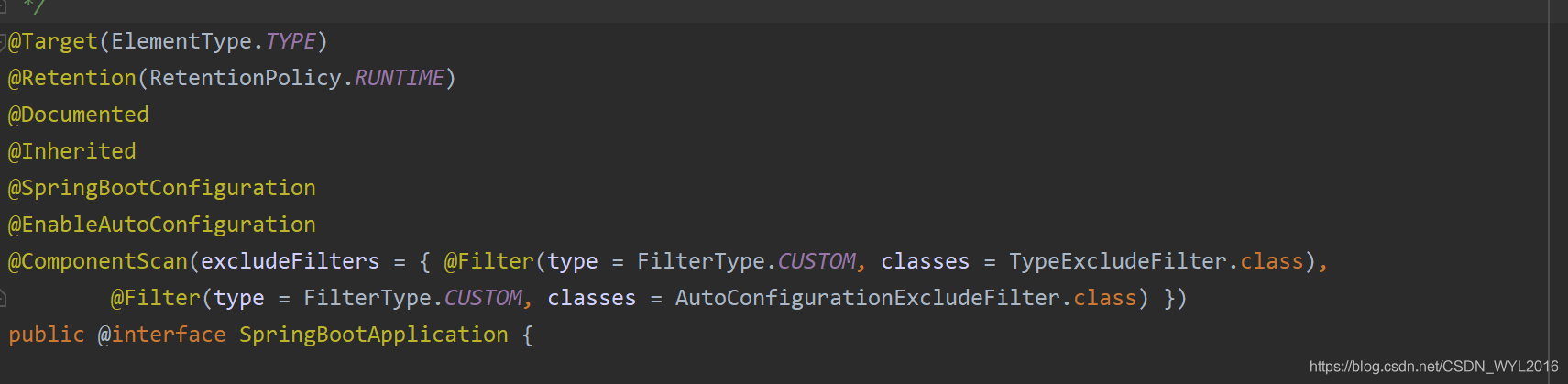
@Import注解
继续进入@EnableAutoConfiguration注解中,看到Import注解,了解spring的就知道spring会扫描到AutoConfigurationImportSelector这个类,这个类实现了DeferredImportSelector接口
public class AutoConfigurationImportSelector implements DeferredImportSelector, BeanClassLoaderAware, ResourceLoaderAware, BeanFactoryAware, EnvironmentAware, Ordered DeferredImportSelector是ImportSelector的子类,实现了这个接口的类,spring就会执行到process,selectImports这个两个方法。
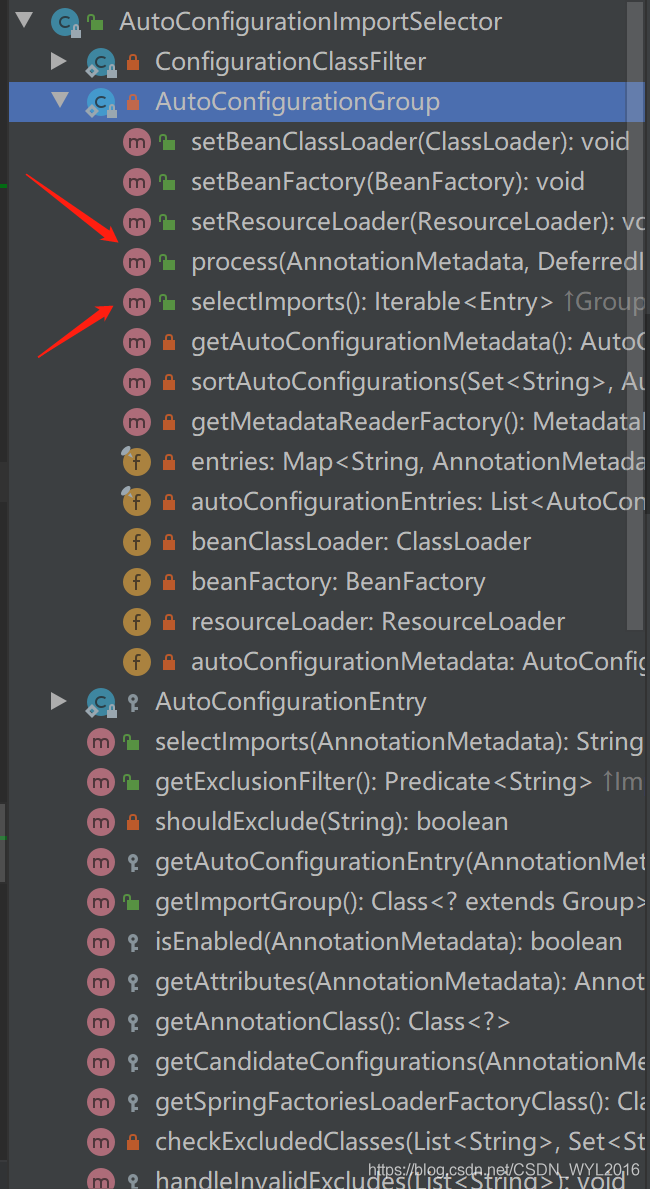
process方法
public void process(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata, DeferredImportSelector deferredImportSelector) { Assert.state(deferredImportSelector instanceof AutoConfigurationImportSelector, () -> String.format("Only %s implementations are supported, got %s", AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class.getSimpleName(), deferredImportSelector.getClass().getName())); AutoConfigurationEntry autoConfigurationEntry = ((AutoConfigurationImportSelector) deferredImportSelector) //处理需要自动配置的 .getAutoConfigurationEntry(annotationMetadata); this.autoConfigurationEntries.add(autoConfigurationEntry); for (String importClassName : autoConfigurationEntry.getConfigurations()) { this.entries.putIfAbsent(importClassName, annotationMetadata); } } /** * Return the {@link AutoConfigurationEntry} based on the {@link AnnotationMetadata} * of the importing {@link Configuration @Configuration} class. * @param annotationMetadata the annotation metadata of the configuration class * @return the auto-configurations that should be imported */ protected AutoConfigurationEntry getAutoConfigurationEntry(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) { if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) { return EMPTY_ENTRY; } AnnotationAttributes attributes = getAttributes(annotationMetadata); //返回候选的配置集合 List<String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes); configurations = removeDuplicates(configurations); Set<String> exclusions = getExclusions(annotationMetadata, attributes); checkExcludedClasses(configurations, exclusions); configurations.removeAll(exclusions); configurations = getConfigurationClassFilter().filter(configurations); fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents(configurations, exclusions); return new AutoConfigurationEntry(configurations, exclusions); } /** * Return the auto-configuration class names that should be considered. By default * this method will load candidates using {@link SpringFactoriesLoader} with * {@link #getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass()}. * @param metadata the source metadata * @param attributes the {@link #getAttributes(AnnotationMetadata) annotation * attributes} * @return a list of candidate configurations */ protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) { //通过SPI的方法,加载,启动时在run方法中已经加载过了 //getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass这个方法返回的就是EnableAutoConfiguration.class List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(), getBeanClassLoader()); Assert.notEmpty(configurations, "No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you " + "are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct."); return configurations; } protected Class<?> getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass() { return EnableAutoConfiguration.class; } public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryType, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) { String factoryTypeName = factoryType.getName(); //之前在构造方法中加载时,EnableAutoConfiguration已经被加载过了,所以这边直接可以从map中获取 return loadSpringFactories(classLoader).getOrDefault(factoryTypeName, Collections.emptyList()); } 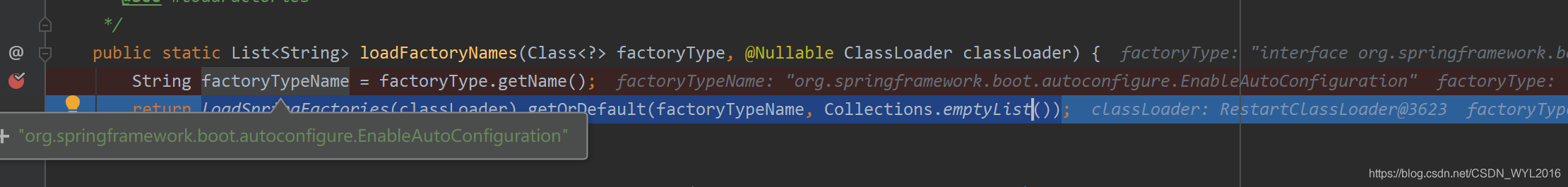
private static final Map<ClassLoader, MultiValueMap<String, String>> cache = new ConcurrentReferenceHashMap<>(); cache的key是classLoader,value又是一个map,其中key是EnableAutoConfiguration,value是spring.factories文件中对应的内容
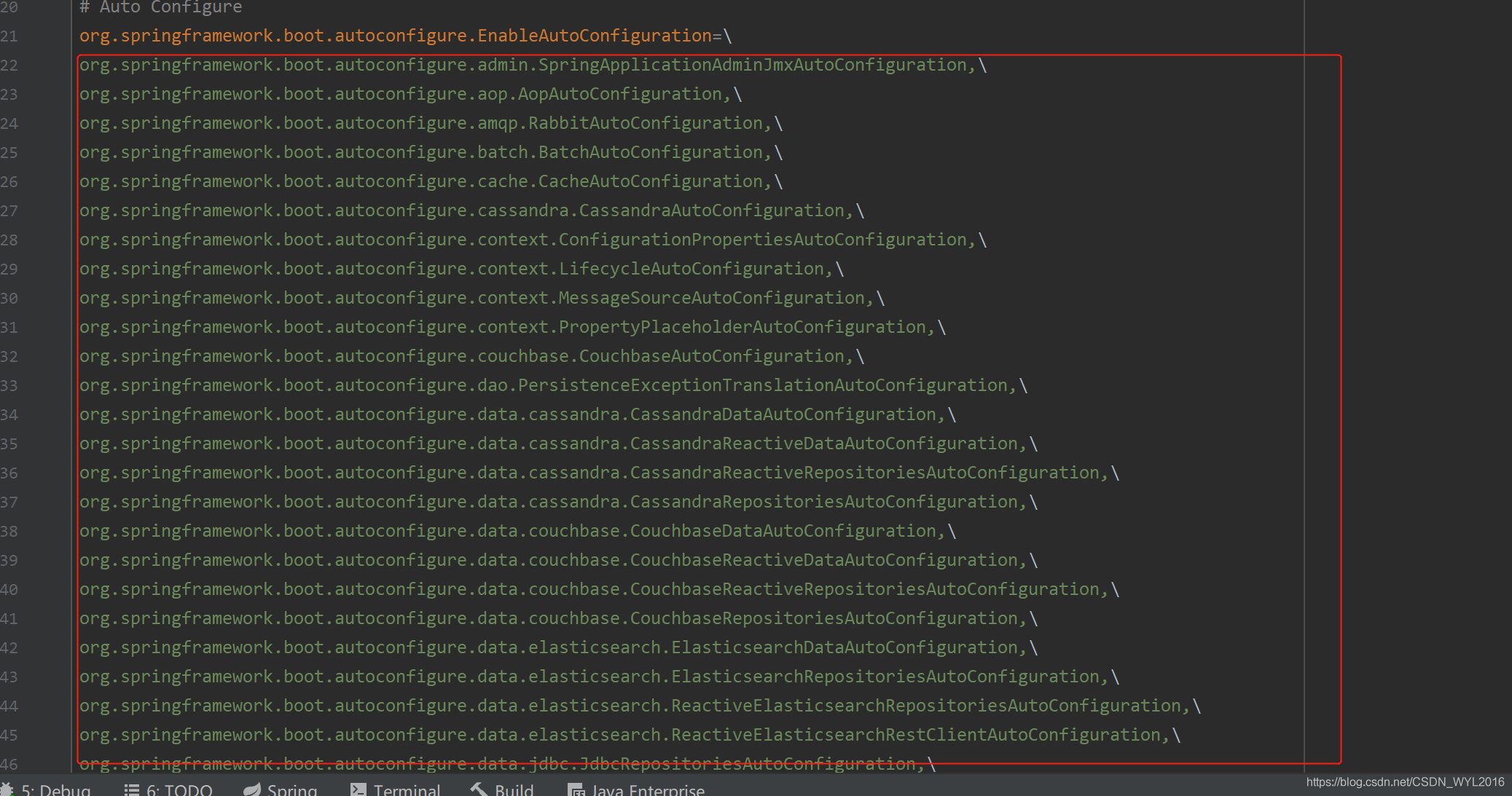
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) { //直接从cache中获取 MultiValueMap<String, String> result = cache.get(classLoader); if (result != null) { return result; } try { Enumeration<URL> urls = (classLoader != null ? classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION) : ClassLoader.getSystemResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION)); result = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>(); while (urls.hasMoreElements()) { URL url = urls.nextElement(); UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url); Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource); for (Map.Entry<?, ?> entry : properties.entrySet()) { String factoryTypeName = ((String) entry.getKey()).trim(); for (String factoryImplementationName : StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String) entry.getValue())) { result.add(factoryTypeName, factoryImplementationName.trim()); } } } cache.put(classLoader, result); return result; } catch (IOException ex) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [" + FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION + "]", ex); } } 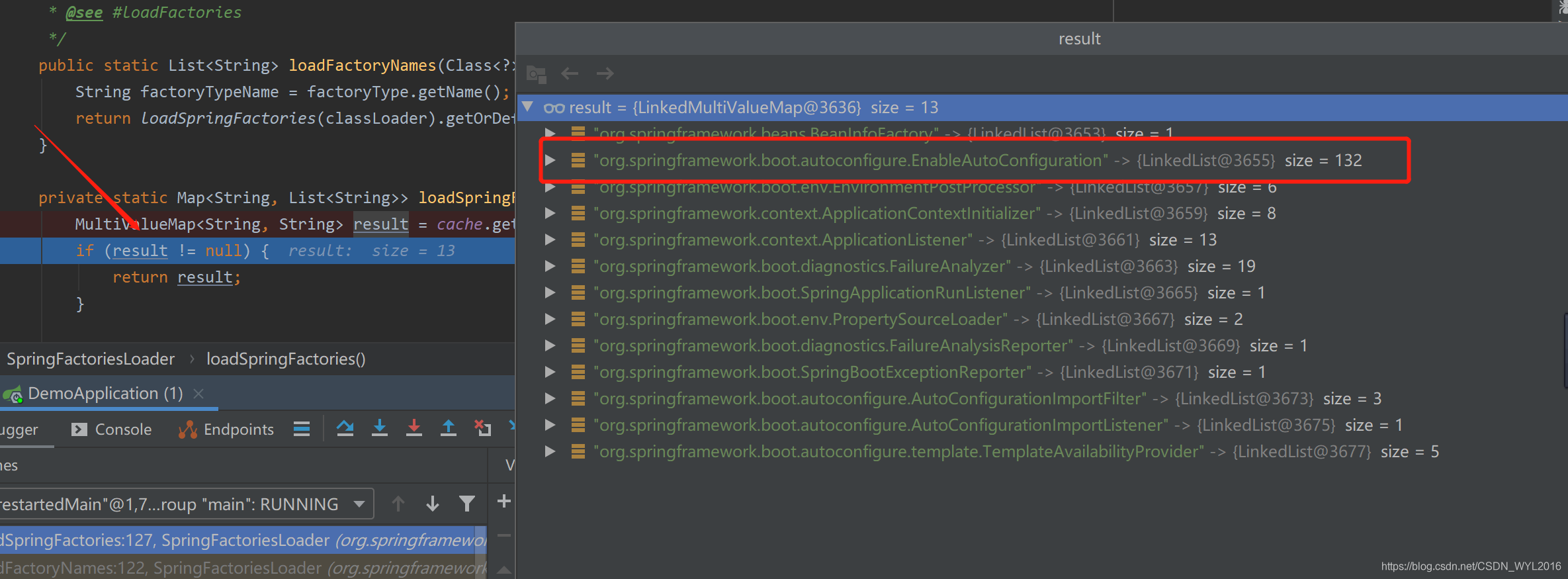
selectImports方法
这个方法主要就是封装了,把上面从factories文件中获取到的信息,封装成一个个Entry对象。
@Override public Iterable<Entry> selectImports() { if (this.autoConfigurationEntries.isEmpty()) { return Collections.emptyList(); } Set<String> allExclusions = this.autoConfigurationEntries.stream() .map(AutoConfigurationEntry::getExclusions).flatMap(Collection::stream).collect(Collectors.toSet()); Set<String> processedConfigurations = this.autoConfigurationEntries.stream() .map(AutoConfigurationEntry::getConfigurations).flatMap(Collection::stream) .collect(Collectors.toCollection(LinkedHashSet::new)); processedConfigurations.removeAll(allExclusions); return sortAutoConfigurations(processedConfigurations, getAutoConfigurationMetadata()).stream() .map((importClassName) -> new Entry(this.entries.get(importClassName), importClassName)) .collect(Collectors.toList()); } 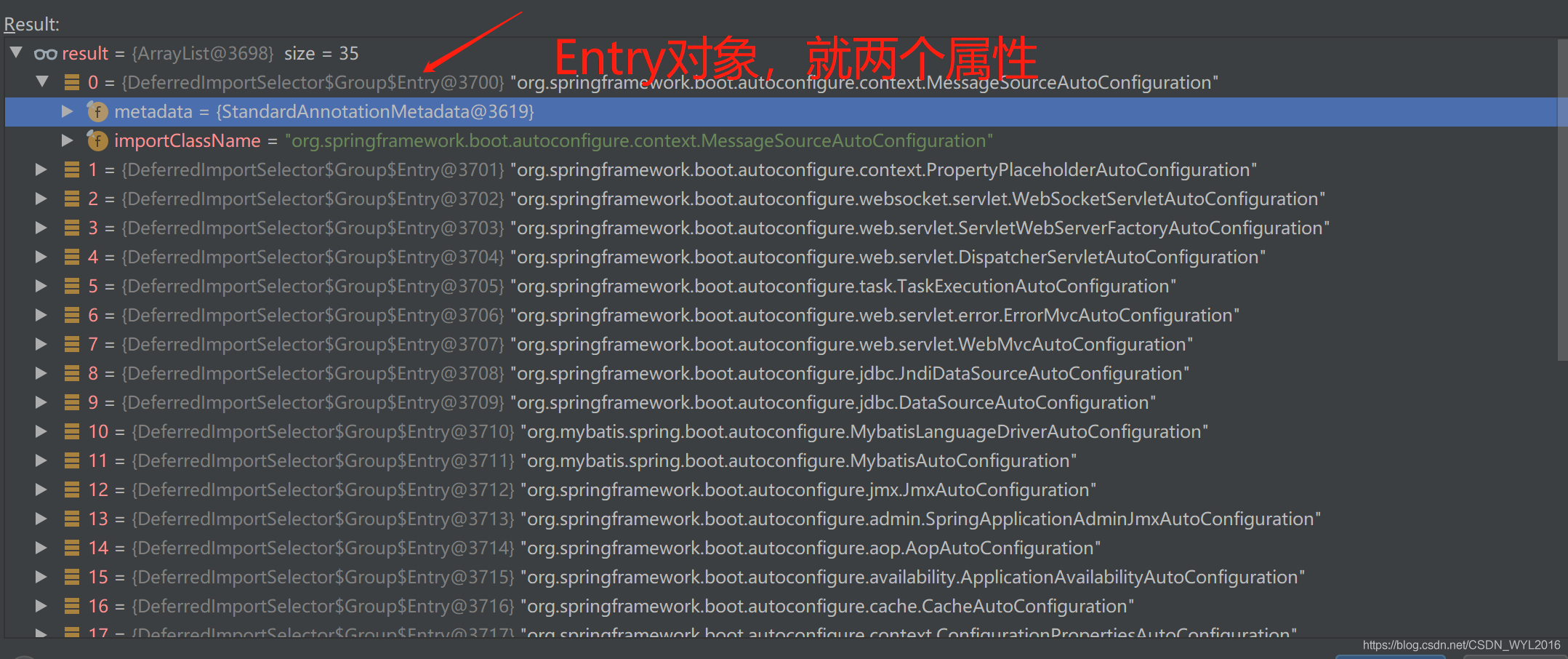
从刚刚的构造方法回来后,继续跟进run方法
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?>[] primarySources, String[] args) { return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args); } SpringBoot的主流程方法
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) { StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch(); stopWatch.start(); ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null; Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>(); configureHeadlessProperty(); SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args); listeners.starting(); try { ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments( args); ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments); configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment); Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment); context = createApplicationContext(); exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances( SpringBootExceptionReporter.class, new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context); prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner); // 其他方法就不看了,这个方法就会进入核心的refresh()方法中 refreshContext(context); afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments); stopWatch.stop(); if (this.logStartupInfo) { new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass) .logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch); } listeners.started(context); callRunners(context, applicationArguments); } catch (Throwable ex) { handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners); throw new IllegalStateException(ex); } try { listeners.running(context); } catch (Throwable ex) { handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null); throw new IllegalStateException(ex); } return context; } 好了,到此后续的流程就是由ConfigurationClassPostProcessor把这些从factories文件中收集到的类,封装成BeanDefinition并加载到spring容器中了,这完全是Spring IOC部分的知识了,入口在refresh方法 —> invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors的方法,
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors这个方法主要可以完成对有@Configuration 、@Component 、@Bean 、@ComponentScan 、@Import 、@ImportResource注解的收集,此处就不做深入解析了。
上一个:vue初始化动画加载
下一个:Parquet列式文件存储格式
热门文章
- 宠物粮食批发进货渠道有哪些呢图片视频介绍(宠物粮食批发进货渠道有哪些呢图片视频介绍大全)
- 3月16日→21.6M/S|2025年最新免费节点QV2ray Node订阅链接地址
- Spring Cloud Eureka(三):认识Eureka Server 与 Eureka Client
- 哪里有领养小猫小狗的地方 哪里有领养小猫小狗的地方啊
- 加盟狗粮加工厂赚钱吗 加盟狗粮加工厂赚钱吗现在
- 开宠物美容店需要具备哪些条件和条件(开宠物美容店挣钱吗)
- 长沙宠物猫领养中心在哪里 长沙宠物猫领养中心在哪里啊
- 4月1日→20.7M/S|2025年最新免费节点QV2ray Node订阅链接地址
- 4月18日→19.1M/S|2025年最新免费节点QV2ray Node订阅链接地址
- 3月11日→20M/S|2025年最新免费节点QV2ray Node订阅链接地址